SQE2 - Dispute Resolution Outline
Are you overwhelmed by the masses of dispute resolution information you are expected to know? With contract law and tort, thrown into the mix as well?
Do you have no time to revise, let alone make concise notes?
Do you just want a bullet-pointed summary of the exact topics that you need to know?
Then, you are in the
SQE2 Dispute Resolution Outline
contains summaries in bullet-point format of:
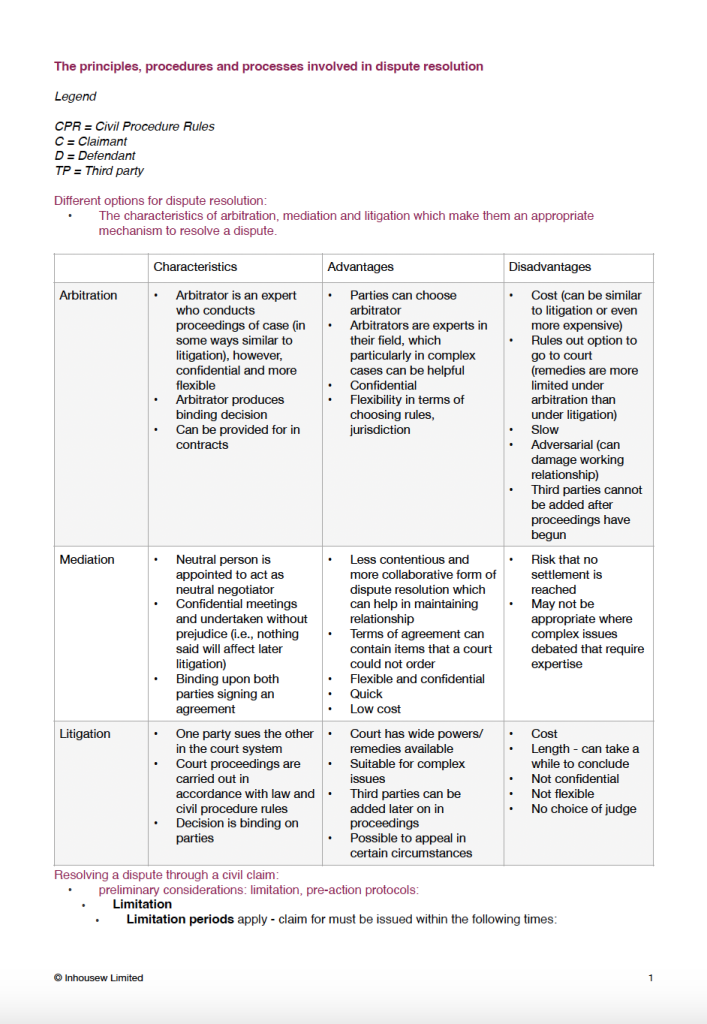
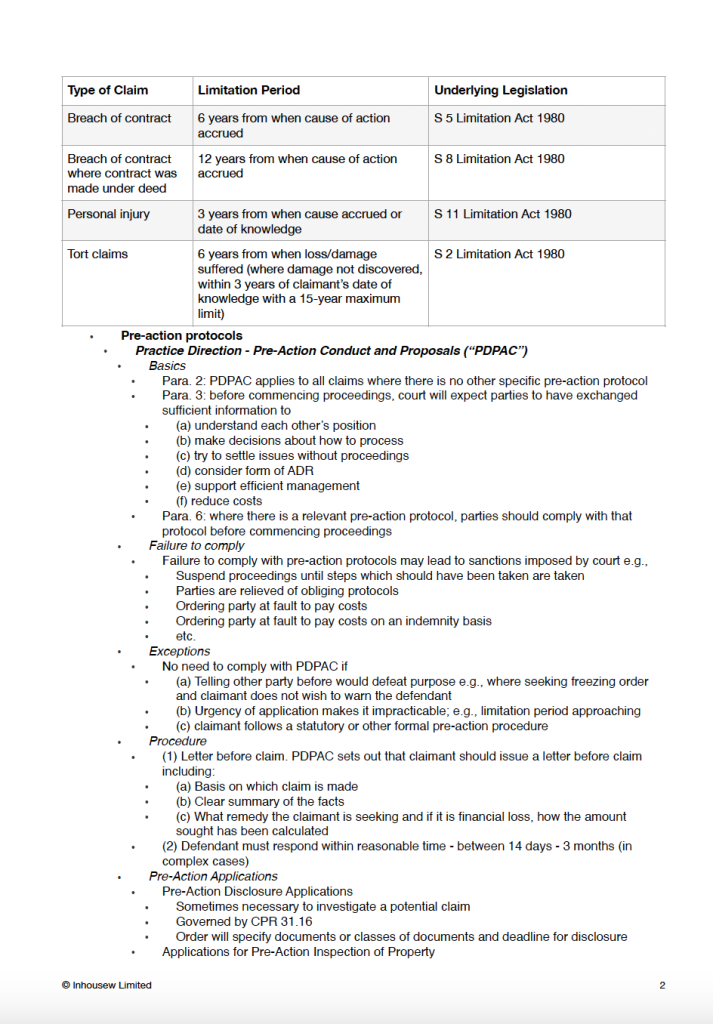
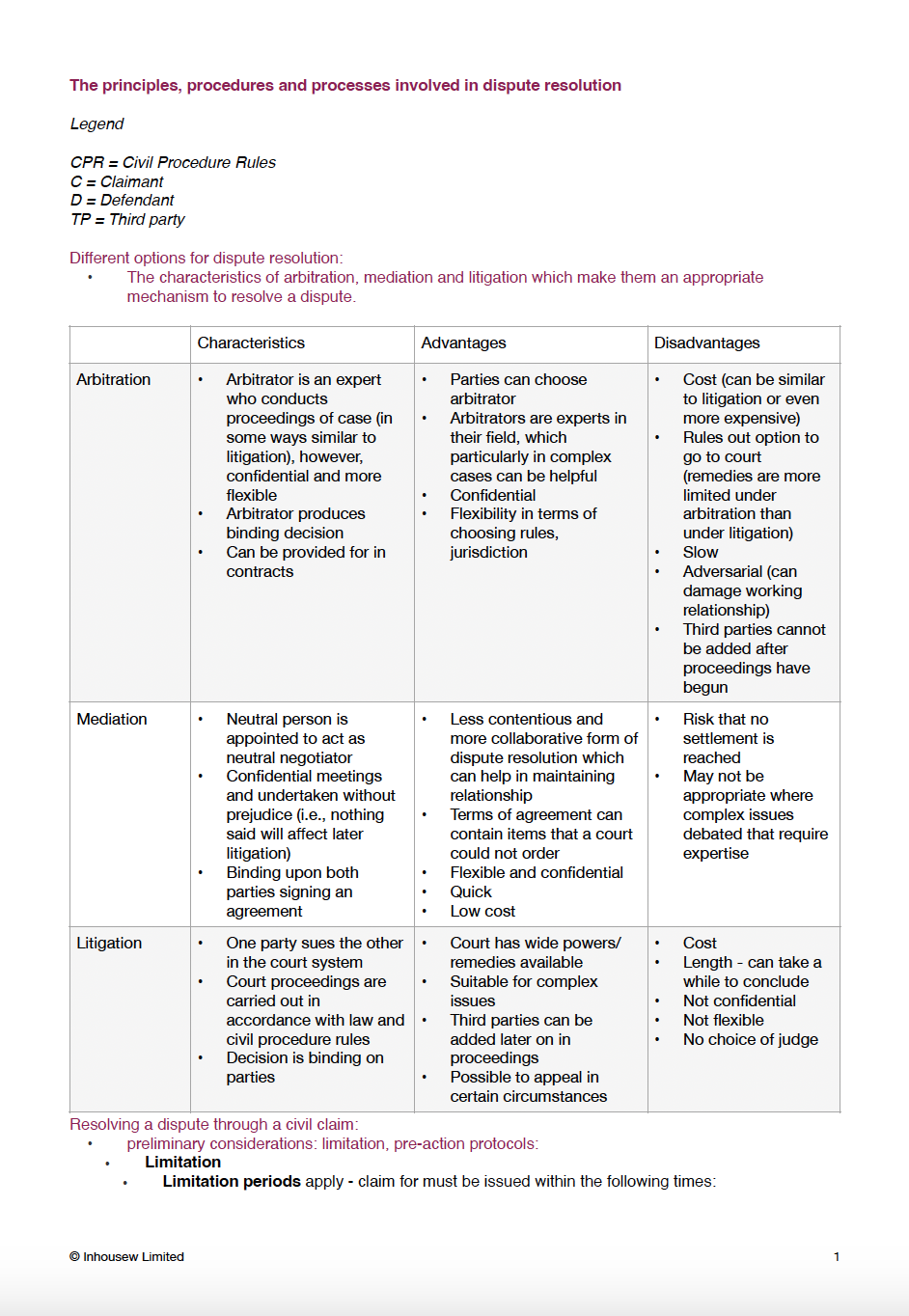
All topics listed by the SRA in the FLK for Dispute Resolution
Why SQE2 Outlines?
Easy revision tool to help you test yourself quickly
Created by someone who passed the SQE2 first time
Increase chances of covering everything that may come up on the exam
What does the SQE2 Dispute Resolution Outline cover?
The SQE2 Dispute Resolution Outline contains the entire functioning knowledge specified by the SRA in relation to Dispute Resolution, Tort and Contract Law for the SQE2.
What is the SQE2?
The SQE2 exam is the second of two "super" exams required by the Solicitors Regulation Authority in order to qualify as a solicitor of England and Wales.
The SQE2 exam contains the following assessments:
- Written Part
- Day 1 - Dispute Resolution and Criminal Procedure
- Day 2 - Property and Wills
- Day 3 - Business Law
- Oral Part
-
- Day 1 - Dispute Resolution and Property
- Day 2 - Criminal Procedure and Wills
Each day of the written part includes:
- Case & Matter Analysis (60min)
- Legal Writing (30min)
- Legal Research (60min)
- Legal Drafting (45min)
Each day of the oral part includes:
- Advocacy (45min prep and 15min presentation)
- Client Interviewing (10min prep, 25min interviewing, and 25min writing an attendance note by hand)
Who will teach me?

Hi there
My name is Madeleine Weber!
I have been working as a legal professional for half a decade, predominantly in the IT industry as an in-house counsel in the UK.
I qualified as a solicitor via the transitional arrangements by sitting the QLTS MCT and the SQE2.
I passed the first ever SQE2 exam on my first attempt in 2022.
Whilst preparing for the exam, I really wished I had concise revision notes to revise from. I didn't have much time to make revision notes, and the notes I purchased from the prep course providers were incredibly lengthy.
That is what inspired me to write out concise and easy to follow notes based on the Functioning Legal Knowledge required by the SRA.
Testimonials
FAQ
This is a very subjective question and will depend on your background and education.
I personally would recommend to purchase a SQE2 preparation course, as this will provide you with all the tools to have the best chance to pass on your first attempt.
My SQE2 outlines should be relied on as supplementary revision aides.
You will have access for 1 year from the date of purchase.
A summary of all the topics listed by the SRA in relation to criminal law and procedure that may be tested on the SQE2.
All materials are downloadable and usable offline.
The course is provided via Teachable. All materials will be available on all your devices either via a web browser or via the Teachable app.
If you are unhappy about any aspect of the course, do let me know and I will do my best to sort the issue out for you.
Otherwise, there is no refund policy for this item.